The compounds P, Q and S
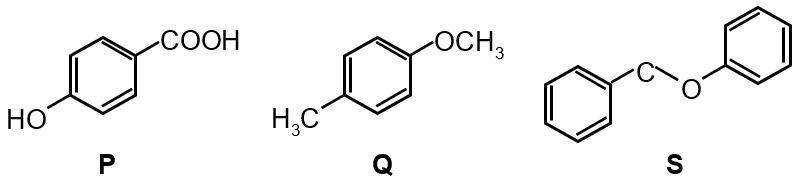
were separately subjected to nitration using HNO3 / H2SO4 mixture. The major product formed in each case respectively, is
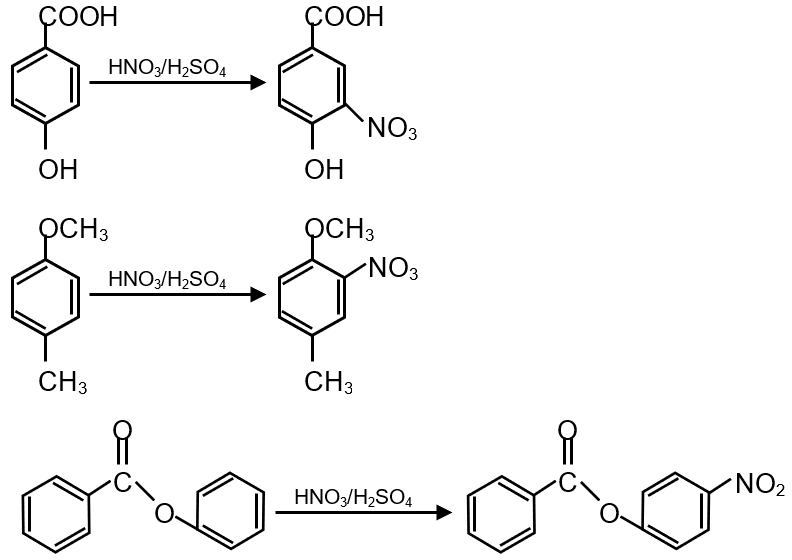
This question involves predicting the major nitration products for three aromatic compounds (P, Q, S) using HNO3/H2SO4 (nitrating mixture). Nitration is an electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction where a nitro group (-NO2) is introduced. The position of substitution depends on the existing substituents on the benzene ring, which can be activating (ortho/para directing) or deactivating (meta directing).
Step 1: Analyze each compound's substituent effects
Compound P has a -NHCOCH3 (acetanilide) group. The -NHCOCH3 is an ortho/para director because the nitrogen lone pair is conjugated into the ring (though less activating than -NH2 due to carbonyl withdrawal). Nitration occurs primarily at the para position (ortho is sterically hindered).
Compound Q has a -NO2 group. Nitro group is strongly deactivating and meta-directing. Nitration will occur meta to the nitro group.
Compound S has a -Cl group. Chlorine is deactivating due to electronegativity but ortho/para directing due to lone pair resonance. Nitration occurs at ortho and para positions, with para often favored due to sterics.
Step 2: Predict the major product for each
For P: Major product is para-substituted relative to -NHCOCH3.
For Q: Major product is meta-substituted relative to -NO2.
For S: Major product is para-substituted relative to -Cl (ortho is possible but para is less sterically hindered).
Step 3: Match with options
Review the given options to identify which one shows:
Final Answer: The correct option is the one where P has para-nitro, Q has meta-nitro, and S has para-nitro substitution.
Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution: Reactions like nitration, halogenation, sulfonation follow this mechanism. The directing effects depend on substituents:
Key Theory: Substituents affect electron density via resonance and inductive effects. Ortho/para directors donate electrons (or have lone pairs), while meta withdraw electrons.