Which of the following is correct structure of tyrosine?
The structure of Tyrosine amino acid is
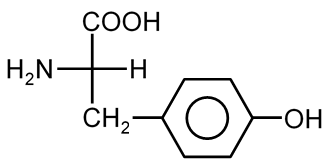
Tyrosine is an amino acid, which are the building blocks of proteins. It has a specific structure consisting of a central carbon atom (the alpha carbon) bonded to:
For tyrosine, the R group is a phenolic group, which is a benzene ring with a hydroxyl (-OH) group attached. This makes tyrosine aromatic and polar. The correct structure must show this specific side chain attached to the standard amino acid backbone.
The standard amino acid backbone can be represented as: , where the "CH" represents the alpha carbon. For tyrosine, the R group attached to this carbon is (a phenol group).
Therefore, the correct structure is the one where a benzene ring with an -OH group is attached to the CH group of the amino acid. You must look for the option where the side chain is a phenol (benzene with OH) and not any other group like a simple phenyl (benzene without OH) or an incorrect substituent.
Amino Acids: Organic compounds containing both amine (-NH2) and carboxylic acid (-COOH) functional groups, along with a side chain specific to each amino acid. They are classified based on the properties of their R groups (non-polar, polar, acidic, basic).
Tyrosine Specifics: Its IUPAC name is (2S)-2-Amino-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propanoic acid. The phenolic OH group makes it a polar amino acid. It is a precursor to important neurotransmitters and hormones.
General Amino Acid Formula: The basic structure can be generalized as , where R represents the variable side chain.