The correct statement for the molecule, CsI3 is:
Cs+ and I3–
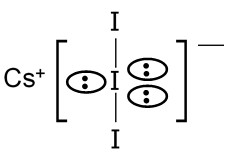
The correct statement for the molecule CsI3 is that it contains Cs+ and I3– ions. This is because CsI3 is an ionic compound formed by cesium (Cs) and the triiodide ion (I3–). Cesium, being an alkali metal, readily loses one electron to form Cs+ ion. Iodine can form polyhalide ions like I3–, which is linear and symmetric, consisting of three iodine atoms with a negative charge. The compound is not covalent, nor does it contain Cs3+ or free I2 molecules; it is purely ionic with Cs+ and I3– as the constituent ions.
Polyhalide Ions: These are ions formed by the combination of halogens, such as I3–, ICl2–, etc. They are stable due to the large size and high polarizability of iodine atoms.
Ionic Compounds: Formed by the transfer of electrons from metal to non-metal, resulting in positively charged cations and negatively charged anions held together by electrostatic forces.
Formula for Triiodide Ion: I3– is represented as , and its structure is linear: I–I–I.