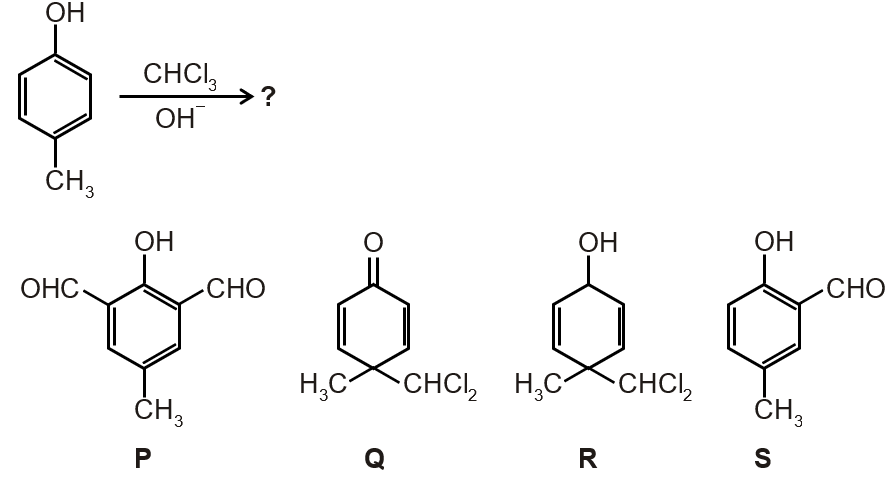
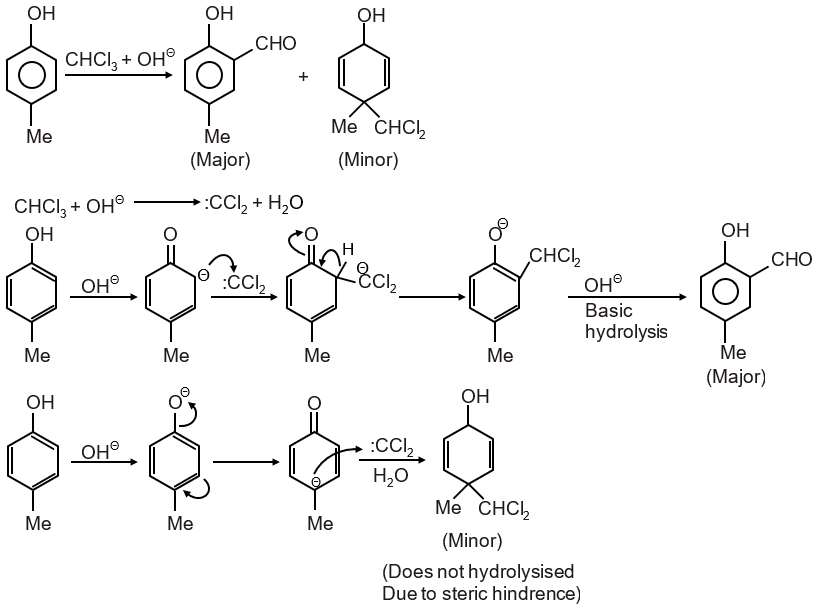
In the following reaction, the product(s) formed is(are)
This question involves predicting the major and minor products in an electrophilic addition reaction of an alkene with HBr, specifically considering the stability of carbocation intermediates and Markovnikov's rule.
The given reactant is a cyclic alkene with a double bond. When HBr adds to an unsymmetrical alkene, the electrophile (H⁺) attaches to the less substituted carbon, forming the more stable carbocation intermediate. The bromide ion then attacks this carbocation.
Step 1: Protonation of the double bond
The alkene reacts with H⁺. Two possible carbocations can form:
The tertiary carbocation is more stable due to hyperconjugation and inductive effects.
Step 2: Nucleophilic attack
Br⁻ attacks the carbocation. For the tertiary carbocation, attack can occur from two sides:
Thus, the major product is the one where Br adds anti to the methyl group (less steric hindrance), and the minor product is where Br adds syn to the methyl group.
Based on the options:
Therefore, the products are P (major) and R (minor).
Electrophilic Addition: Reactions where an electrophile adds to a double or triple bond, common in alkenes and alkynes.
Markovnikov's Rule: In the addition of HX to an unsymmetrical alkene, the hydrogen atom attaches to the carbon with more hydrogen atoms.
Carbocation Stability: Order of stability: tertiary > secondary > primary > methyl. Stability influences the reaction pathway and product distribution.
No specific mathematical formulae, but key concepts: