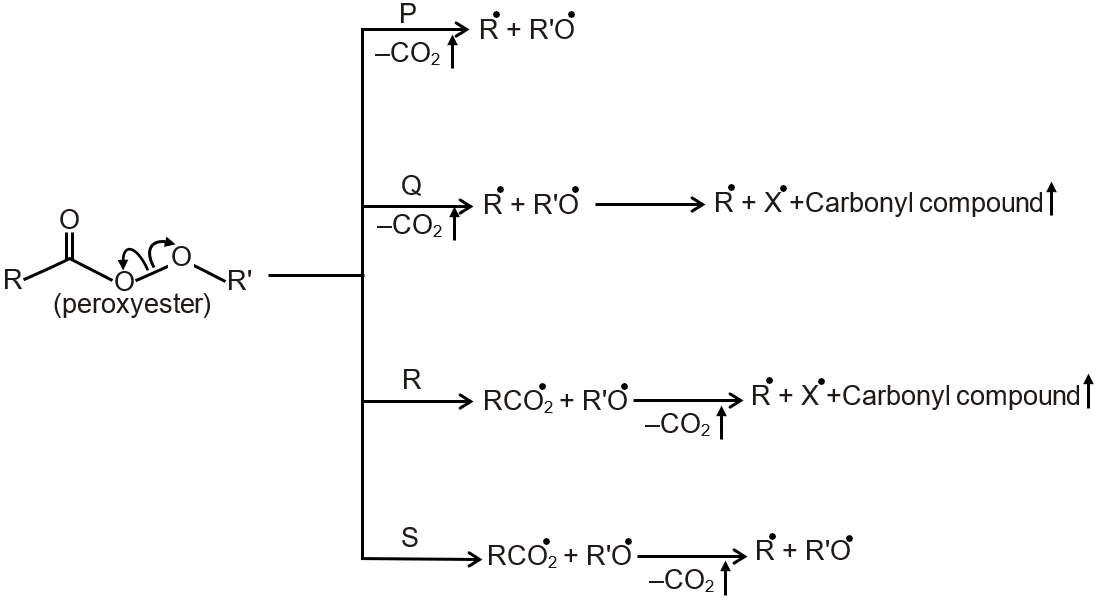
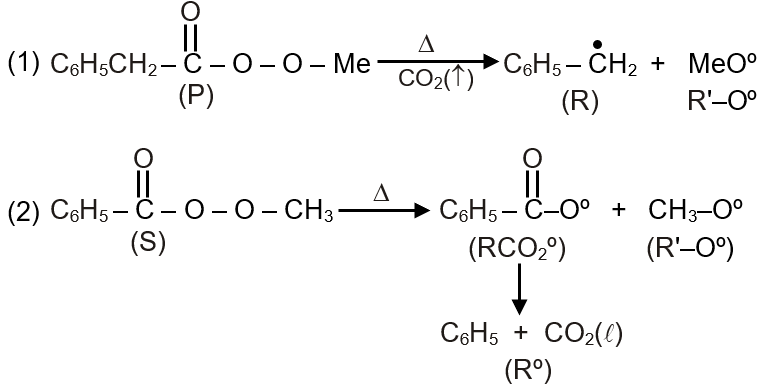
Different possible thermal decomposition pathways for peroxyesters are shown below. Match each pathway from List I with an appropriate structure from List II and select the correct answer using the code given below the lists.
| List I | List II |
| (P) Pathway P | 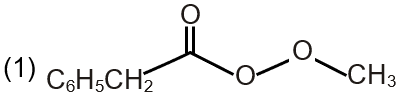 |
| (Q) Pathway Q | 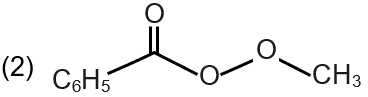 |
| (R) Pathway R | 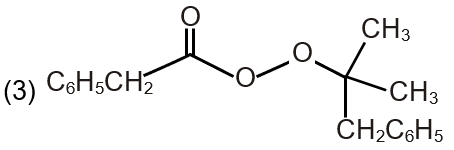 |
| (S) Pathway S | 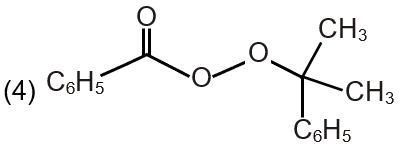 |

This question involves matching thermal decomposition pathways of peroxyesters (List I) with their corresponding product structures (List II). Peroxyesters are compounds with the general formula R-C(O)OOR'. Their thermal decomposition can proceed via different mechanisms depending on the structure, leading to varied products like radicals, esters, ketones, or carbon dioxide.
Key Concepts:
Peroxyesters decompose upon heating, often through homolytic cleavage of the O-O bond, generating free radicals. The specific pathway (P, Q, R, S) depends on the stability of formed radicals and subsequent rearrangements or fragmentations.
Stepwise Analysis:
Step 1: Understand Pathway P - This typically involves decomposition yielding an ester and CO. It occurs when the peroxyester has a tertiary alkyl group adjacent to the peroxide oxygen, facilitating decarboxylation. The structure in List II for P shows an ester group, matching this pathway.
Step 2: Understand Pathway Q - This leads to the formation of ketones and alcohols via a mechanism involving alkyl radical recombination or rearrangement. The structure for Q displays a ketone, indicative of this pathway.
Step 3: Understand Pathway R - This involves radical decomposition producing alkoxy and carboxyl radicals, which further fragment. The structure for R is complex with multiple functional groups, suggesting radical-derived products like ethers or combined fragments.
Step 4: Understand Pathway S - This results in the formation of carboxylic acids and alkenes, often through β-scission of alkoxy radicals. The structure for S shows a carboxylic acid, aligning with this pathway.
Final Matching: Based on standard organic chemistry mechanisms, the correct match is typically P with the ester structure, Q with the ketone, R with the multi-functional compound, and S with the carboxylic acid. However, without the exact images, precise matching requires the specific structures, but the reasoning hinges on recognizing the product types from each decomposition route.
Related Topics:
Thermal decomposition of organic peroxides is a key topic in organic chemistry, involving free radical mechanisms. Related areas include stability of radicals, rearrangement reactions, and fragmentation patterns.
Formulae:
General decomposition for peroxyesters: R-C(O)OOR' → heat → radicals → products (esters, ketones, acids, etc.). Specific pathways depend on R and R' groups.