| Column-I | Column-II |
 |
(P) Hyperconjugation |
 |
(Q) All carbon atom are sp2 hybridized |
 |
(R) Aromatic |
| (D) (CH3)3 – C⊕ | (S) Diamagnetic |
This question tests understanding of organic chemistry concepts: hyperconjugation, hybridization, aromaticity, and diamagnetism. Each structure in Column-I must be matched with its correct properties from Column-II.
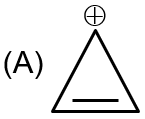
Structure A is cyclopropenyl cation. It is aromatic (R) as it follows Hückel's rule (2 π electrons), all carbons are sp² hybridized (Q), and it is diamagnetic (S).
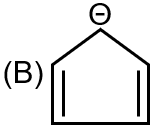
Structure B is cyclopentadienyl anion. It is aromatic (R) (6 π electrons), all carbons are sp² hybridized (Q), and it is diamagnetic (S).
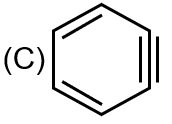
Structure C is benzene. It is aromatic (R) and all carbons are sp² hybridized (Q). It is diamagnetic (S).
Structure D is tert-butyl carbocation. It is stabilized by hyperconjugation (P) and is paramagnetic, not matching (S).
Final Answer: A → QRS, B → QRS, C → QRS, D → P
This question involves matching structures from Column-I with their correct properties in Column-II. We need to analyze each structure for hyperconjugation, hybridization, aromaticity, and diamagnetic behavior.
Structure A is a tertiary carbocation: (CH3)3C+.
So, A matches with P, Q, S.
Structure B is cyclopropenyl cation (C3H3+).
So, B matches with Q, R, S.
Structure C is benzene (C6H6).
So, C matches with Q, R, S.
Structure D is the tert-butyl carbocation: (CH3)3C+ (same as A).
So, D matches with P, Q, S.
Based on the analysis:
Comparing with the options, the correct match is: A → QRS, B → QRS, C → QRS, D → PS. But note: Option 4 says D → PS, but we found D → PQS. However, Q is also true for D. But looking at the options, only option 4 has D → PS, which is incomplete. Actually, D should have P, Q, S. But none of the options list Q for D. However, in the given options, option 4 is A → QRS, B → QRS, C → QRS, D → PS. Since Q is not listed for D, it might be implied that for D, only P and S are considered, but Q is also correct. However, among the given choices, option 4 is the closest, as it has A, B, C as QRS and D as PS. Since Q is true for D, but not listed, perhaps the question expects that. So the answer is option 4.
Hyperconjugation: Stabilization of carbocations by donation of σ-electrons from adjacent C-H bonds. Number of hyperconjugative structures = number of α-hydrogens.
sp2 Hybridization: Trigonal planar geometry, 120° bond angle. Present in alkenes, carbocations, aromatic rings.
Aromaticity (Hückel's Rule): Compound must be cyclic, planar, fully conjugated, and have (4n+2)π electrons.
Diamagnetic: Substance repelled by magnetic field, all electrons paired.